PREDICTIVE AI: SEMANTIC VS FEATURE
SEGMENTATION:
2022-02 Pablo Lorenzo-Eiroa's
Research on Artificial Intelligence activates
differences between predictive AI and generative AI through semantic
and visual feature segmentation training repositories implementing
their own Big Data surveys. The research aims at redefining history
through a new way of looking at space and the object of
architecture. A new theory of architecture through Big Data emerges
in which the new lenses of obserbation derive into a new theory of
the object. Insights into the forensic survey, meassurement,
segmentation and prediction enabled the research to find new
boundaries and relationships between the work of Borromini's San
Carlo and Rainaldi's SM in Campitelli. The prediction AI estimation
is based on global repositories and personal research repositories
designed to train machine vision feature recognition. The research
identifies architectural features in the historic critical
integration of Rainaldi of the work of Borromini and Palladio.
The project proposes to displace assumed
heritage and deconstruct colonizations implicit in the history of
architecture through new theories on the object. The project looks
both into eurocentric heritage to deconstruct possible conflicts and
also non eurocentric architecture in Latin America and parts of the
global
south.
EXANDING POSSIBLE PASTS TO REDEFINE
ARCHITECTURE POSSIBLE FUTURES: The project develops a new theory on
the object through analytical Big Data patterns and machine vision
not possible for the naked eye, looking for non-intuitive Big Data
patterns insights able to deconstruct conventional cultural readings
of the project. By implementing AI the project aims to both expand
the history of archtiecture through observations on the object that
could not happen otherwise. Usually the history of architecture is
defined by istorians that developed theories based on readings,
historic documentation and other means such as measurement and
observation. We propose to develop new insights redefining the
existing theories of the object by forensic evidence, developing non
intuitive expanded observations. We therefore propose a new theory
of architecture recomipling and crissing references with all
existing histories and expanding into new theories of architecture
never drawn.
AUGMENTED REALITY AND "DIGITAL TWINS":
the project is both a research project and a project in itself
rethinking the future from expanding the past. The
project is part of e-Architects and Pablo Lorenzo-Eiroa's research
to expand Big Data repositories for historic preservation including
environmental concerns. The project aims at refunctionalizing
existing heritage, buildings and cities in relation to augmented
reality making them fully navigable online and to train AI
repositories and ANN. Pablo Lorenzo-Eiroa's research also includes
generative AI over surveyed point cloud repositories, developing
unique artistic environments and projective creative immersive
environments.
CREDITS:
survey SM Campitelli by Carlo Rainaldi by Andrew
Saunders with the assistance of Pablo Lorenzo-Eiroa and Mario
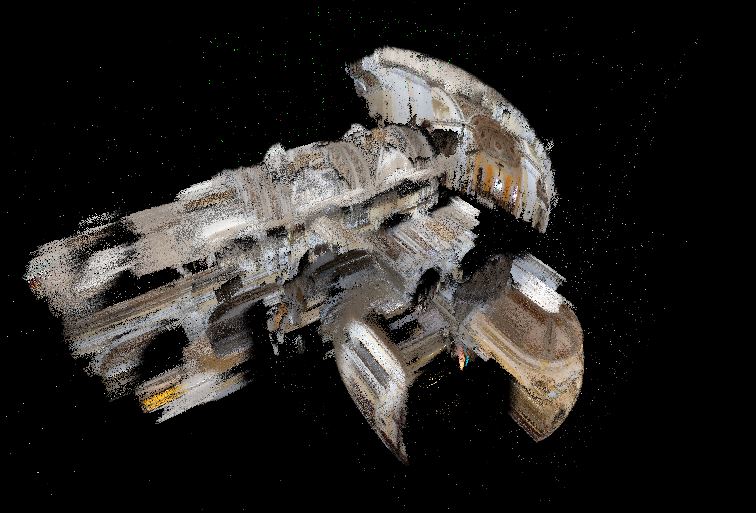
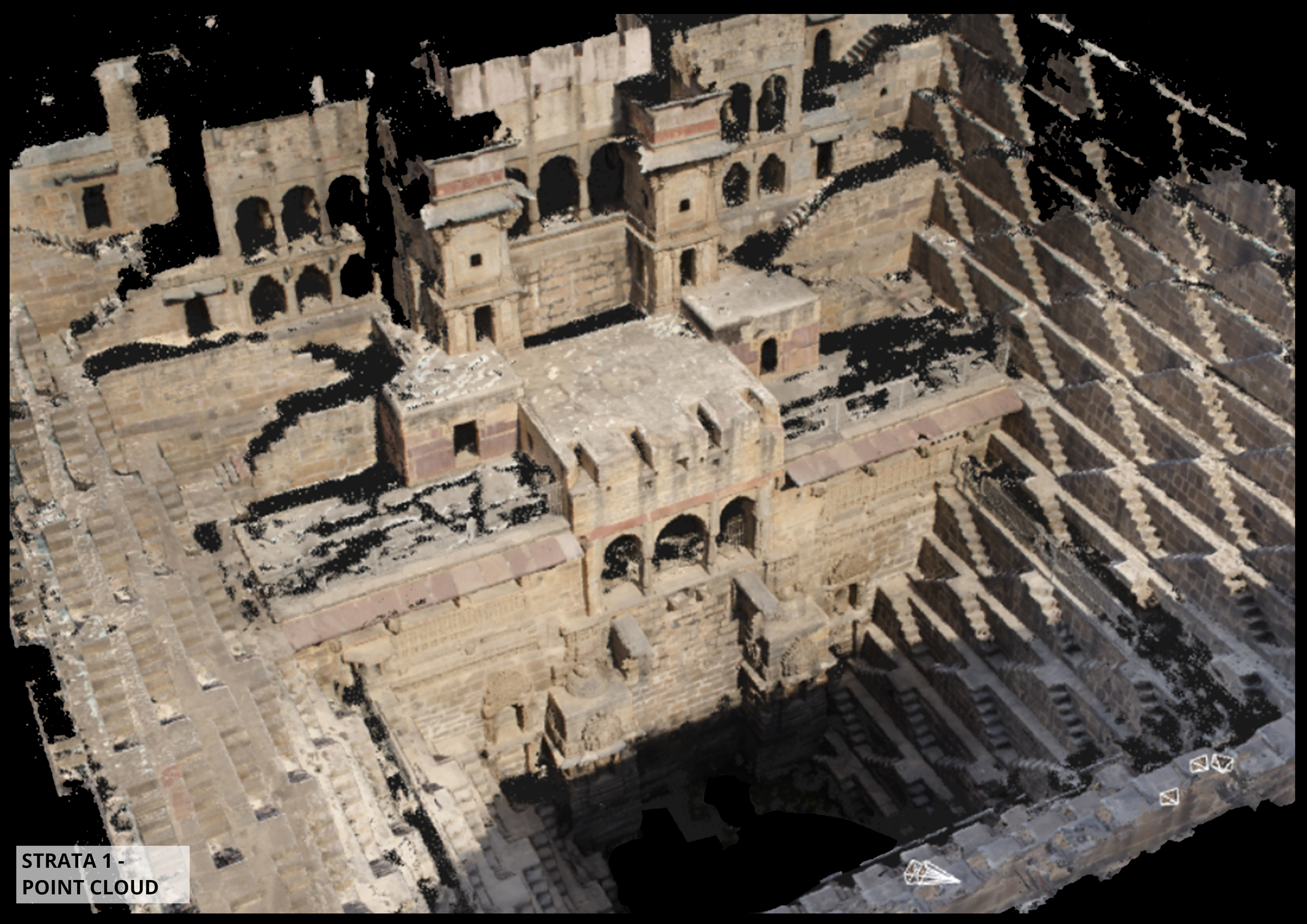
Graziano Valenti (2015). The result point cloud of LiDAR laser
scanning using FARO M70 scanner is processed by Pablo Lorenzo-Eiroa
through multiple platforms and interfaces, including Scene and
others (2015-2022). Some processing was done by Pablo Lorenzo-Eiroa
PI with Rsearch Assistant Salma Kattass (2021-22). Point cloud 250M
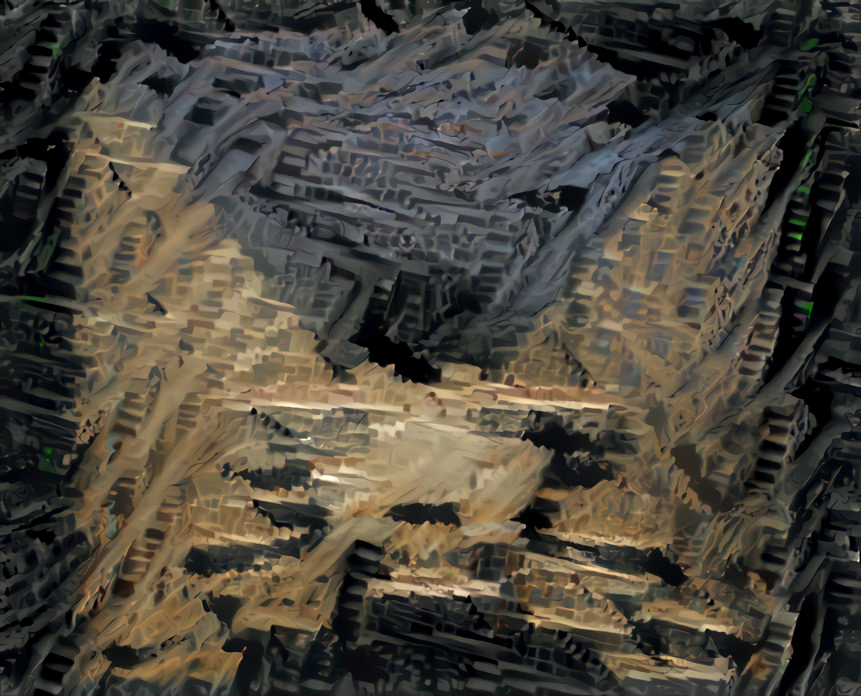
points; estimation prediction based on 50,000 points and training on
a reduced repository of 1000 points through several cycles.
The
research was published in the book of May of 2023.
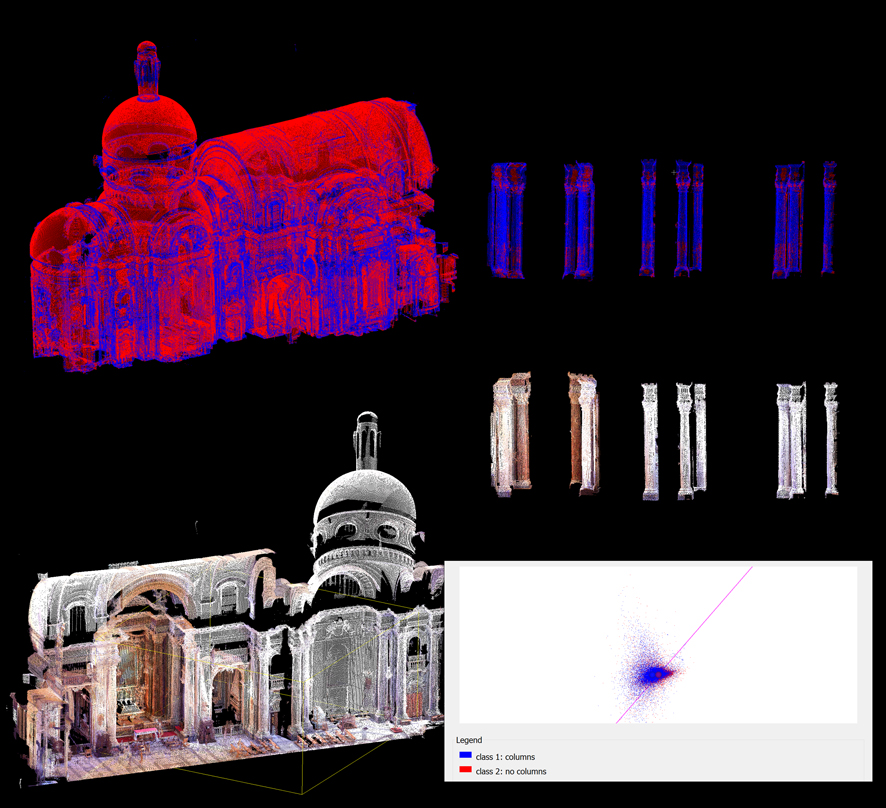
AI
machine vision semantic segmentation prediction
For more information and description of the
research and findings refer to the book
"Digital Signifiers in an Architecture of Information: From Big Data
and Simulation to Artificial Intelligence", Pablo Lorenzo-Eiroa,
Routledge, London 2023: